Services
Water Treatment Components
for Services!
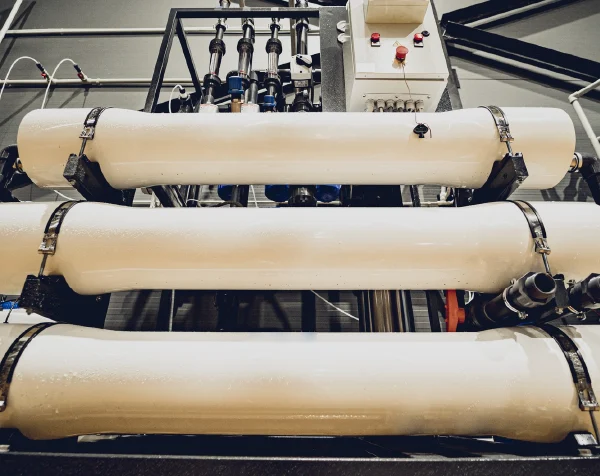


Membrane Housing
Membrane housing is typically a protective casing used in water filtration systems, particularly in reverse osmosis (RO) units. It houses the semipermeable membrane, which is the core component responsible for filtering out contaminants from the water. The housing helps ensure that the membrane stays in place is properly sealed, and remains protected from damage.
There are several types of membrane housings, including ones for residential, commercial, and industrial filtration systems. They are often made from durable materials such as fiberglass-reinforced plastic or stainless steel.
Applications :
Key Features of Membrane Housing :
Corrosion Resistance :
Especially important in marine environments or systems dealing with chemically aggressive substances.
Pressure Resistance:
Membrane housings are designed to withstand the high pressures required for reverse osmosis filtration.
Compatibility:
Membrane housings are designed to fit specific sizes and types of RO membranes.
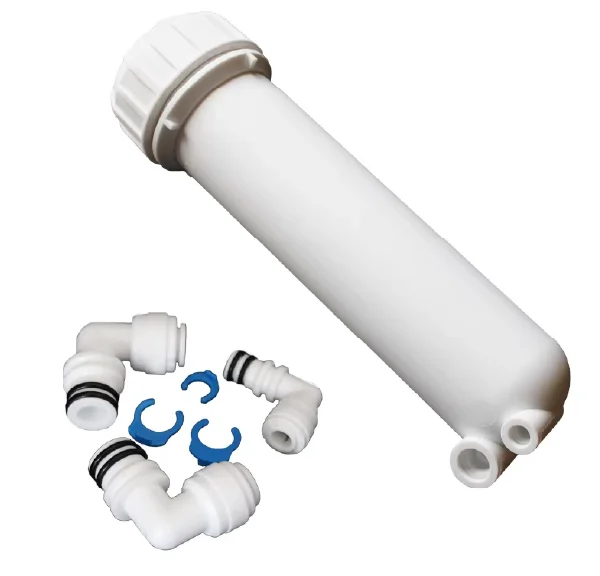

Membrane Housing spares
Saddle Strap (4″ & 8″) :
These are typically used to securely hold and mount the membrane housings in place, ensuring that the housing is fixed and stable during operation. The 4″ and 8″ sizes likely refer to the diameter of the membrane housing they fit.
FC Port (Feed/Concentrate Port) :
These are the ports, usually made from stainless steel, where water enters or exits the membrane housing. Stainless steel is often used because of its durability and resistance to corrosion, especially in water filtration systems.
Saddle Strap (4″ & 8″) :
Application :
The saddle strap is used to secure the membrane housing to a mounting bracket or frame. It typically fits around the membrane housing to hold it in place, preventing movement and ensuring a stable system.
Use :
The size (4″ and 8″) indicates the diameter of the membrane housing. Different sizes are needed depending on the size of the membrane used in the filtration system. These straps help reduce vibration and movement, which could cause damage to the system or affect performance.
Material :
These are often made of durable plastic, stainless steel, or other corrosion-resistant materials to withstand the pressure and conditions of water filtration systems.
FC Port (Feed/Concentrate Port) :
Application :
The stainless steel port is a crucial connection point for the membrane housing. Ports allow water to flow in and out of the housing, facilitating the filtration process.
Use :
These ports are typically used to connect the feed water, permeate (filtered water), and concentrate (wastewater) lines to the membrane housing. They allow for controlled water pressure and flow through the membrane during filtration.
Material :
Stainless Steel is used for these ports due to its resistance to corrosion, especially in high-pressure and potentially acidic or alkaline environments like reverse osmosis systems.
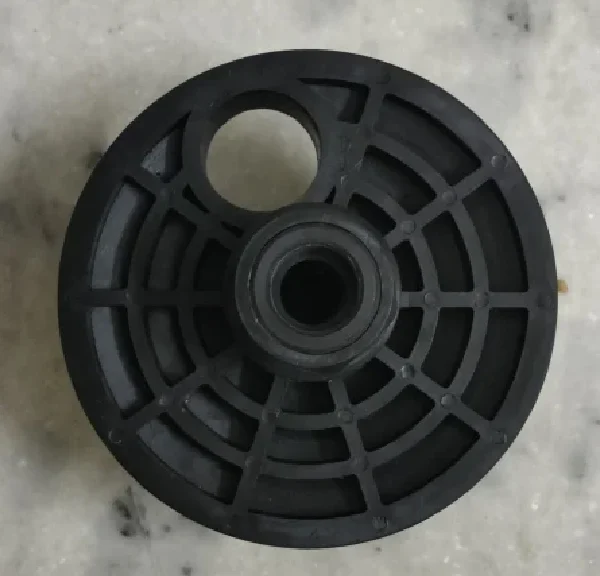

8” & 4” End Cap Assembly
Sealing and Containing the Membrane :
The end cap covers the two ends of the membrane housing and ensures that the membrane is securely in place. It prevents any leaks or bypasses of water, ensuring that all water is forced through the membrane for filtration.
Pressure Containment :
Membrane housings in filtration systems operate under pressure, and the end caps are designed to handle this pressure. They prevent any pressure loss, which could reduce filtration efficiency.
Flow Regulation :
Some end caps have specific features (such as ports for inlet/outlet) that help manage the flow of water through the housing, ensuring it follows the correct path for optimal filtration.
Features :
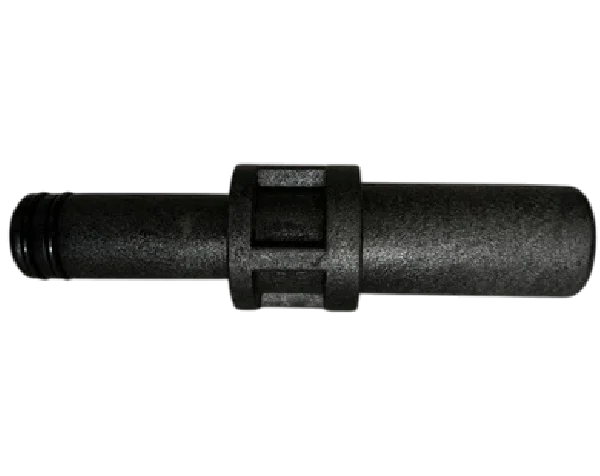

End Cap Spares
Item list :
Application & Use :
The end caps seal the membrane housing from both ends, ensuring the integrity of the system and preventing water from bypassing the membrane.
Membrane housings typically operate under high pressure, so the end caps help to withstand this pressure and maintain the system’s stability.
End caps often have specific ports for water to enter and exit, as well as ports for monitoring and other system functions like pressure relief.
Over time, end caps may become damaged due to wear and tear, so having spare end caps ensures that you can replace them quickly to avoid system downtime.
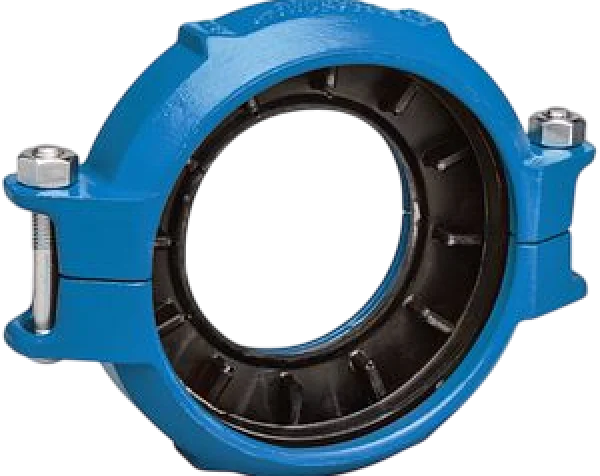

Victaulic Coupling
Size Range : From 3/4″ to 8″
Materials :
- MOC (Material of Construction) : Stainless Steel (304, 316), Duplex Stainless Steel, Super Duplex Stainless Steel, Cast Iron (CI), and PVC
Pressure Ratings : 300 psi to 1200 psi
Key Features of Victaulic Couplings :
Corrosion Resistance :
Stainless steel (304, 316) and duplex/super duplex materials offer excellent resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for use in harsh or corrosive environments.
High Pressure :
The pressure ratings (from 300 to 1200 psi) suggest these couplings are suitable for high-pressure applications, often in industrial piping systems.
Variety of Materials :
The wide range of material options allows for use in different industries—PVC for lower-pressure applications, CI for more standard industrial uses, and SS for more demanding environments.
Ease of Installation :
One of the main benefits of Victaulic couplings is that they allow for quick, easy installation without the need for welding, threading, or flanging, saving time on-site.
Typical Applications :

Victaulic Coupling Spares
Victaulic Piece (Coupling Body) :
Gasket :
Nut and Bolt :
Operating Temperature: 45º c (max.) Colour Options: Blue
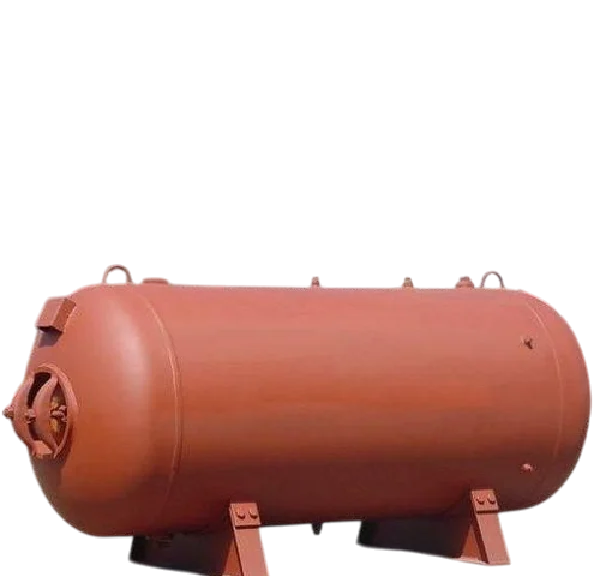

Applications :
| MODAL | CONNECTION | CAPACITY | BASE | |
| TOP OPEN | BOTTOM OPEN | LITERS | ||
| 613 | 2.5” | – | 4.6 | Standard |
| 617 | 2.5” | – | 6.6 | Standard |
| 635 | 2.5” | – | 13.7 | Standard |
| 735 | 2.5” | – | 20.1 | Standard |
| 744 | 2.5” | – | 25.6 | Standard |
| 817 | 2.5” | – | 10.9 | Standard |
| 835 | 2.5” | – | 25 | Standard |
| 844 | 2.5” | – | 32.1 | Standard |
| 1054 | 2.5” | – | 63.3 | Standard |
| 1252 | 2.5” | – | 97 | Standard |
| 1354 | 2.5” | – | 105.3 | Standard |
| 1465 | 2.5” | – | 148.5 | Standard |
| 1465 | 4” | 4” | 148.5 | Tripod |
| 1665 | 2.5” | – | 192 | Standard |
| MODAL | CONNECTION | CAPACITY | BASE | |
| TOP OPEN | BOTTOM OPEN | LITERS | ||
| 1665 | 4″ | 4″ | 192 | Tripod |
| 1865 | 4″ | – | 268 | Standard |
| 1865 | 4″ | 4″ | 268 | Tripod |
| 2162 | 4″ | 4″ | 341 | Tripod |
| 2472 | 4″ | 4″ | 490 | Tripod |
| 3072 | 4″ | 4″ | 735 | Tripod |
| 3672 | 4” | 4″ | 1031 | Tripod |
| 4272 | 6″Flange | 6″ Flange | 1461 | Tripod |
| 4872 | 6″Flange | 6″ Flange | 1890 | Tripod |
| 6079 | 6″Flange | 6″ Flange | 3000 | Tripod |
| 6386 | 6″Flange | 6″ Flange | 3326 | Tripod |
| 7279 | 6″Flange | 6″ Flange | 4577 | Tripod |
| 8079 | 6″Flange | 6” Flange | 5074 | Tripod |
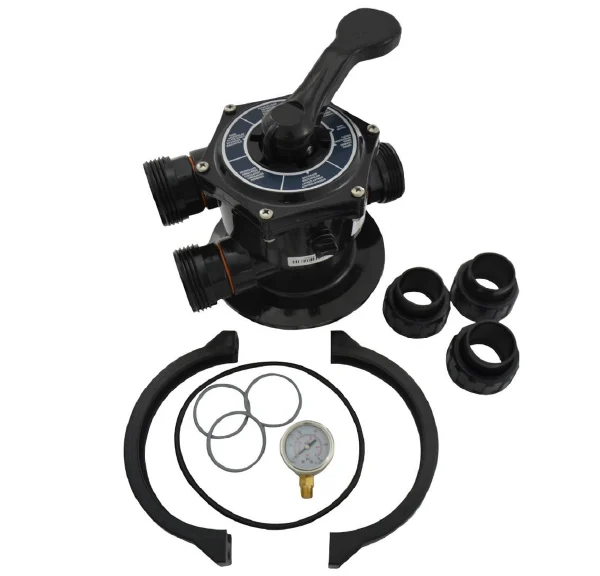

Multiport Value
Distribution System
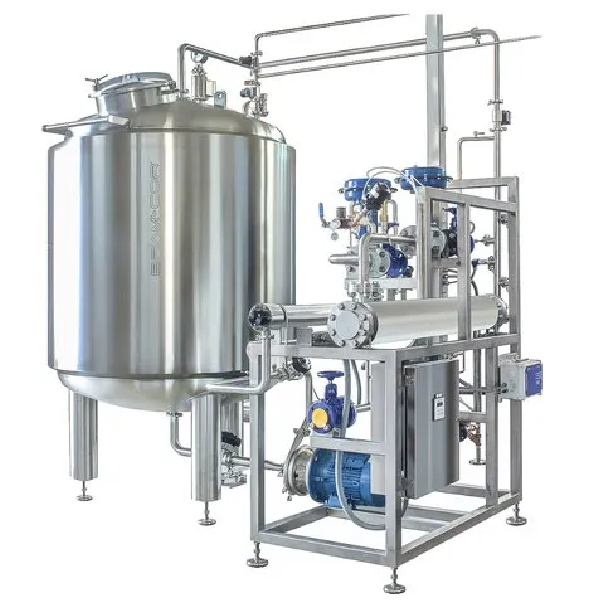

Applications :
| Vessel Diameter | Type of Tank | Description | Type |
| 14″ Upto 36″ Top | 4″ Threaded | Top Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-436-63 |
| 14″(Bottom) | 4″ Threaded | Bottom Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-436-63 |
| 16″(Bottom) | 4″ Threaded | Bottom Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-436-63 |
| 21″(Bottom) | 4″ Threaded | Bottom Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-436-63 |
| 24″(Bottom) | 4″ Threaded | Bottom Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-436-63 |
| 30″(Bottom) | 4″ Threaded | Bottom Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-436-63 |
| 36″(Bottom) | 4″ Threaded | Bottom Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-436-63 |
| 42″(Top) | 6″ Flanged | Top Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-6F42A-75U/76U |
| 48″(Top) | 6″ Flanged | Top Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-6F42A-75U/76U |
| 42″(Bottom) | 6″ Flanged | Bottom Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-6F42A-75U/76U |
| 48″(Bottom) | 6″ Flanged | Bottom Mount Hub & Lateral System | PE-6F42A-75U/76U |
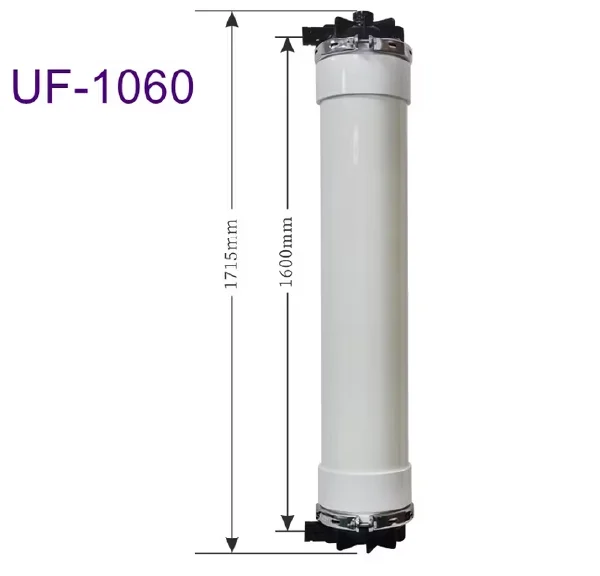

Membrane & UF Element
Proven, reliable, high-performance water purification
Compared to traditional filtration technologies that rely on a screen or filter to remove particles, reverse osmosis (RO) is a pressure-driven separation process that employs a semipermeable membrane and the principles of crossflow filtration.
Reverse osmosis water treatment provides the finest level of filtration. The RO membrane acts as a barrier to all salts and inorganic molecules, as well as organic molecules with a molecular weight greater than approximately 100. It is therefore a highly effective process for removing contaminants such as:
Features :
Application :
Membrane Spares & UF Element Spares
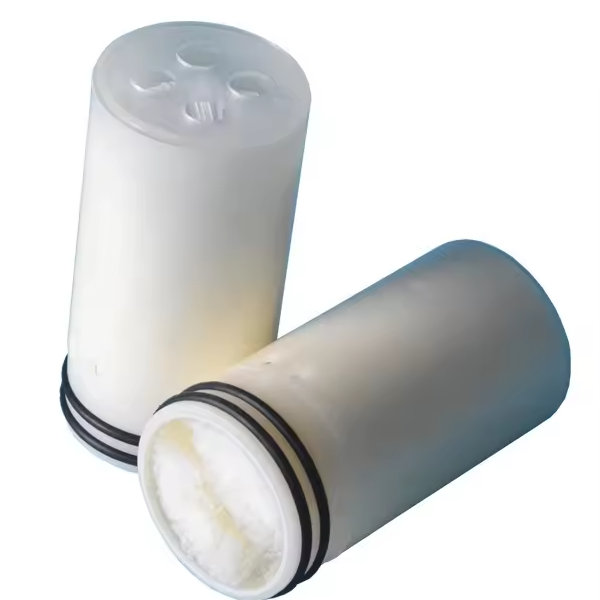

1) Interconnectors for 4040, 8040, BW, and HSRO Membranes:
2) Brine Seal 4″ & 8″ :
Summary of Features:-
3) UF End cap Assembly :
Summary of Features of UF End Cap Assembly :
4) Summary of UF Clamp Features :
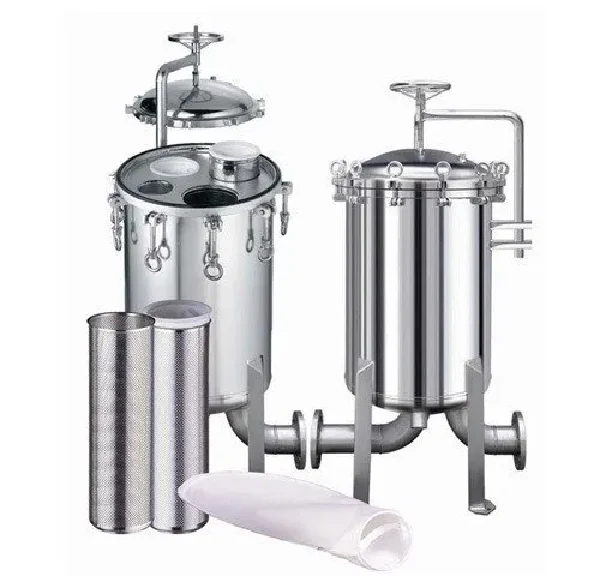

SS Housing
2 Types Of SS Housing:
- SS 304 / SS 316 Cartridge Filter Housings:
SS 304 / SS 316 Cartridge Filter Housing refers to the stainless steel housings used to hold cartridge filters in place within a filtration system. These filter housings are designed to handle different types of filtration media (cartridge filters) for various applications such as water purification, industrial filtration, and chemical processes.
Key Features of SS 304 / SS 316 Cartridge Filter Housings :
Types of SS 304 / SS 316 Cartridge Filter Housings :
Pressure Resistance:
Membrane housings are designed to withstand the high pressures required for reverse osmosis filtration.
Corrosion Resistance :
Especially important in marine environments or systems dealing with chemically aggressive substances.
Compatibility:
Membrane housings are designed to fit specific sizes and types of RO membranes.
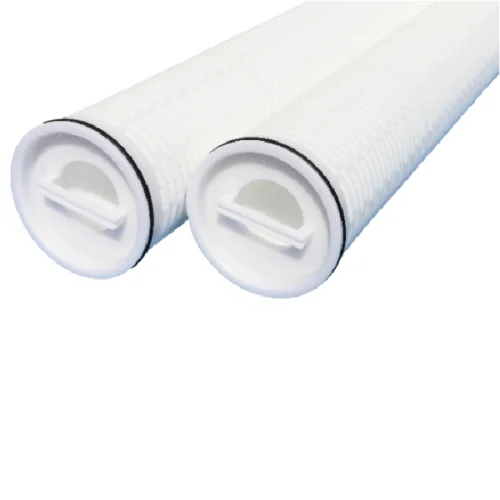

High Flow Filter
Key Features of High Flow Filters :
Types of High Flow Filters :
High Flow Pleated Filters :
These filters use a pleated structure to increase the surface area of the filter material, allowing them to capture more contaminants without restricting the flow. They are used in a wide range of applications, including water and air filtration.
High Flow Cartridge Filters :
Cartridge-style high flow filters are used to filter out particles from liquids or gases. They come in different materials like polypropylene, stainless steel, and activated carbon, depending on the application.
High Flow Bag Filters :
High flow bag filters are used for larger-scale filtration needs. These filters are typically used to filter bulk fluids in industrial systems. They are commonly used in applications like water treatment and chemical processing.
Melt-Blown High Flow Filters :
Melt-blown filters are commonly used for high flow filtration because they are made with fine fiber structures, providing high dirt-holding capacity while maintaining high flow rates.
High Flow Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membrane Filters :
Used in water purification systems, high flow RO membrane filters help separate impurities from water while allowing large volumes of water to pass through quickly.
High Flow Pre-Filters:
Pre-filters are used in filtration systems as an initial filtration step, removing larger particles before the liquid is passed through finer filters. High flow pre-filters are used in water treatment and HVAC systems.
Applications of High Flow Filters :
Benefits of High-Flow Filters:
Increased Efficiency :
High flow filters process larger volumes of fluid without sacrificing filtration quality, helping to meet the demands of large-scale systems.
Improved System Reliability :
These filters can prevent clogs and reduce the frequency of maintenance, making the system more reliable and reducing downtime.
Cost Savings :
Due to their longer lifespan and reduced need for frequent replacements, high flow filters can result in long-term cost savings in both the filtration process and maintenance.
Environmental Benefits :
High flow filters help reduce waste by increasing the efficiency of the filtration process, leading to less frequent disposal of used filters.
Summary of High Flow Filter Features :
High flow filters are essential components in many industrial applications where large volumes of fluid need to be filtered efficiently, without compromising the performance or flow rate of the system. They provide optimal filtration, reduce operational costs, and help maintain the long-term efficiency of filtration systems across a variety of industries.
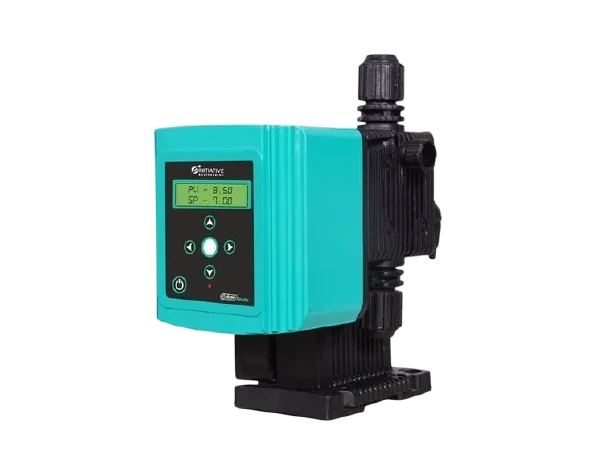

Dosing Pump & Spares
Technical Specification :
| Dosing Rate | Upto 1000 LPH |
| Suction / Discharge Tubing | 4/6 mm, 3/8”, 3/4”,1/2”,1” |
| Pump Head | PP & PVDF |
| Pressure | Upto 10 Kg. |
| Type | Plunger & Moterised |
Features :
Applications :

UPVC – CPVC Pipe & Fittings
UPVC (Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride) and CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes and fittings are both widely used in plumbing and industrial applications. Both materials offer excellent durability, chemical resistance, and ease of installation, but they differ in their specific applications, temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility. Here’s an overview of each:
UPVC is a rigid, non-flexible form of PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride). It is commonly used in water supply systems, sewage systems, and irrigation systems because it offers a cost-effective, reliable, and low-maintenance solution for a wide range of applications.
Corrosion Resistance:
UPVC pipes are highly resistant to corrosion, rust, and chemical degradation, making them ideal for use in environments exposed to water or chemicals.
Lightweight & Easy to Handle :
UPVC pipes are significantly lighter than metal pipes, making them easier to transport and install.
Durability:
These pipes have excellent durability and long service life with minimal degradation over time, even in harsh environments. They can withstand high pressure and are resistant to wear and tear.
Low Thermal Conductivity:
UPVC has low thermal conductivity, making it an excellent material for water temperature regulation.
Smooth Internal Surface :
The smooth internal surface of UPVC pipes reduces friction, ensuring optimal flow rates and reduced pressure loss.
Chemical Resistance:
UPVC is resistant to a wide variety of chemicals, acids, alkalis, and salts, making it suitable for use in chemical processing and wastewater systems.
Non-Toxic:
UPVC is a non-toxic material, making it safe for drinking water applications, as it does not leach harmful substances into the water.
Cold Water Distribution:
UPVC pipes are highly resistant to corrosion, rust, and chemical degradation, making them ideal for use in environments exposed to water or chemicals.
Lightweight & Easy to Handle :
UPVC pipes are significantly lighter than metal pipes, making them easier to transport and install.
Durability:
These pipes have excellent durability and long service life with minimal degradation over time, even in harsh environments. They can withstand high pressure and are resistant to wear and tear.
Low Thermal Conductivity:
UPVC has low thermal conductivity, making it an excellent material for water temperature regulation.
Smooth Internal Surface :
The smooth internal surface of UPVC pipes reduces friction, ensuring optimal flow rates and reduced pressure loss.
Chemical Resistance:
UPVC is resistant to a wide variety of chemicals, acids, alkalis, and salts, making it suitable for use in chemical processing and wastewater systems.
Non-Toxic:
UPVC is a non-toxic material, making it safe for drinking water applications, as it does not leach harmful substances into the water.

Pumps & Spares
Features :
Applications :

Antiscalant
An antiscalant is a chemical additive used to prevent scaling and the formation of mineral deposits in water treatment systems, particularly in reverse osmosis (RO) systems, water softeners, desalination plants, and boilers. These systems are often prone to the buildup of mineral salts like calcium, magnesium, and silica, which can lead to reduced efficiency, clogging, and eventual damage to equipment. Antiscalants are widely used in industrial processes, wastewater treatment, and drinking water production to ensure optimal performance and prevent scaling.
How Antiscalants Work :
Antiscalants function by interfering with the crystallization process of minerals in water. They either inhibit the formation of scale crystals or disperse existing crystals to prevent them from agglomerating and attaching to surfaces. The chemical agents in antiscalants work through various mechanisms:
Threshold Effect:
The antiscalant keeps the minerals in solution even at concentrations that would typically cause them to precipitate. It does so by lowering the nucleation rate of scale formation.
Dispersion:
Antiscalants prevent the growth and agglomeration of crystals, keeping them dispersed in the water, so they do not form solid deposits.
Sequestering:
Antiscalants can “trap” certain ions (such as calcium or iron) in a complex form, which prevents these ions from bonding with others and forming scale.
Crystal Modification:
Flow Meter

Applications :
| DESCRIPTION | CONNECTION |
| 25 TO 250 LPH | 1/2″ BSP (F) |
| 40 TO 400 LPH | 1/2″ BSP (F) |
| 60 TO 600 LPH | 1/2″ BSP (F) |
| 0.1-1 m3/hr | 3/4″ BSP (F) |
| 0.16-1.6 m3/hr | 3/4″ BSP (F) |
| 0.25-2.5 m3/hr | 3/4″ BSP (F) |
| 0.4-4 m3/hr | 1″ BSP (F) |
| 0.6-6 m3/hr | 1″ BSP (F) |
| 0.6-6 m3/hr | 2″ BSP (F) |
| 1-10 m3/hr | 2″ BSP (F) |
| 5-25 m3/hr | 2.5″ BSP (F) |
| 8-40 m3/hr | 2.5″ BSP (F) |
| 12-60 m3/hr | 2.5″ BSP (F) |
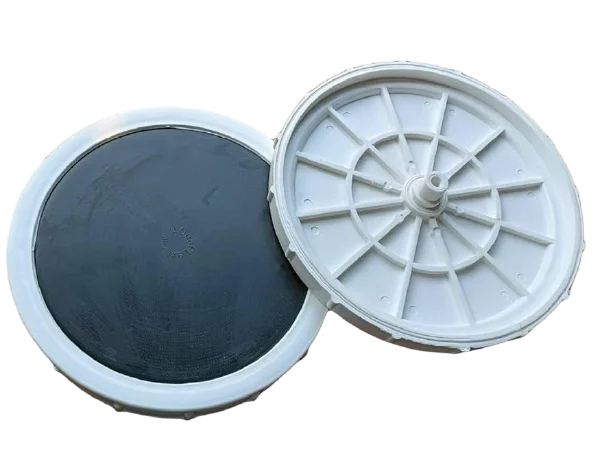

Tube & Disc Diffuser
Application :
Specification :
Working :
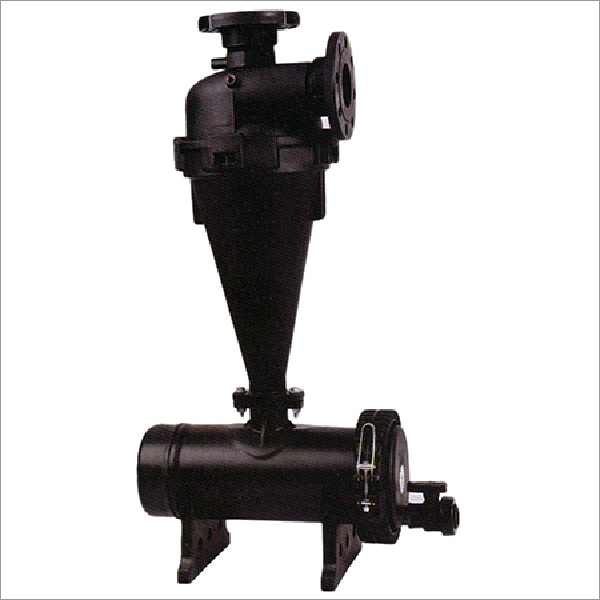

Hydrocyclone Filter
Application :
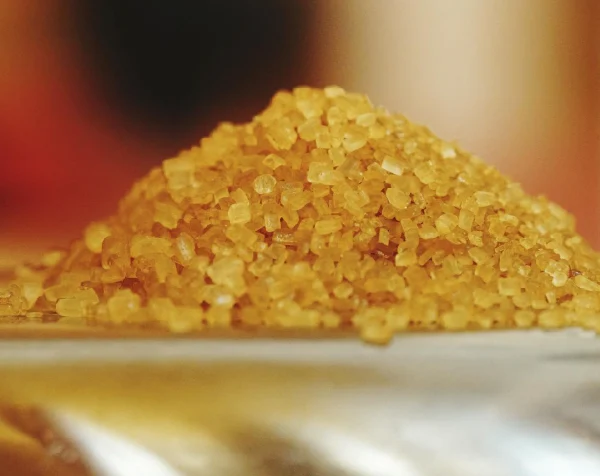

Resins
Types of Resins :
Applications :
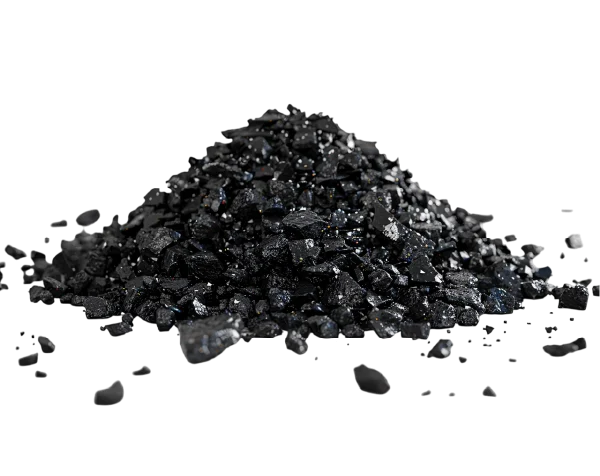

Carbon
Activated carbon is an essential tool in water treatment plants due to its ability to remove organic contaminants, improve taste and odor, and help meet regulatory standards for drinking water. It is used extensively in municipal water treatment, industrial processes, wastewater treatment, and desalination plants to treat various contaminants. While effective and cost-efficient, activated carbon does have limitations, particularly in its inability to remove inorganic substances and the need for regular maintenance. Nonetheless, when used in combination with other treatment technologies like reverse osmosis or chlorination, activated carbon remains an indispensable component of modern water treatment systems.

Media
Different types of filter media are used depending on the raw water quality and the treated water quality required. Be added a filtration system custom made to achieve the turbidity level of less than 1 NTU & suspended solids less than 10 PPM. The filtration beds consist of the coarsest beds, starting from pebbles and sand 0.8 to 1.6 mm in size. filter sand, gravel, & pebbles.

Reverse Osmsis Plant
An Industrial Reverse Osmosis (RO) Plant is a water treatment system designed to purify water on a large scale by removing salts, minerals, contaminants, and other impurities using reverse osmosis technology. It is commonly used in industries where large amounts of clean water are required for manufacturing processes, cooling, or drinking water production.
Overview of an Industrial RO Plant
Feed Water:
The source water, such as municipal water, brackish water, or seawater, is the starting point for the RO process. This water may contain dissolved solids, microorganisms, heavy metals, and other contaminants that need to be removed for specific industrial applications.
Pre-treatment :
Before water enters the reverse osmosis unit, it undergoes pre-treatment to protect the RO membranes from fouling and to ensure optimal performance. Pre-treatment may include:
Reverse Osmosis Membrane:
The heart of the system, the RO membrane is a semi-permeable barrier that allows only pure water molecules to pass through while rejecting larger molecules such as salts, bacteria, and dissolved solids. High pressure is applied to the feed water to push it through the membrane.
High Pressure Pump:
The high-pressure pump boosts the pressure of the incoming water to force it through the RO membrane. The pressure typically ranges between 8-15 bar (116-217 psi), depending on the source water quality.
Permeate and Brine:
Post-treatment:
After passing through the RO membranes, the permeate may undergo additional treatment to ensure the water quality meets specific standards for its intended use. Post-treatment steps may include:
Control and Monitoring Systems:
Advanced automation and monitoring systems are integrated into the RO plant to ensure optimal performance, detect issues like membrane fouling, and control processes like flow rates, pressure, and water quality.
Applications of Industrial RO Plants
Advantages
Challenges
Maintenance Considerations
In essence, an industrial reverse osmosis plant is an essential technology for industries that require purified water in large volumes. By effectively removing contaminants, RO plants help maintain the quality of water used in manufacturing processes, power generation, and other industrial applications.
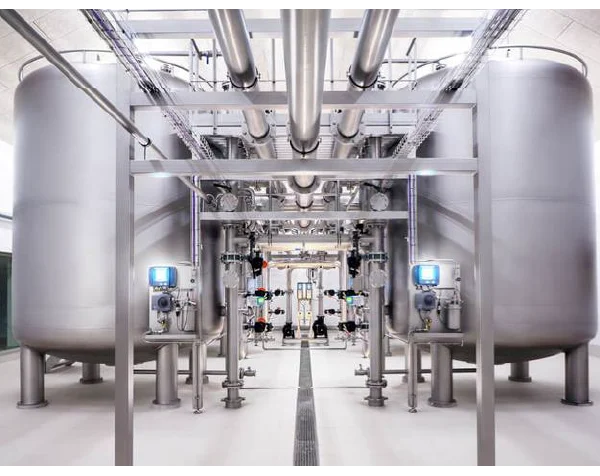

Pressure System
Features :
Applications :
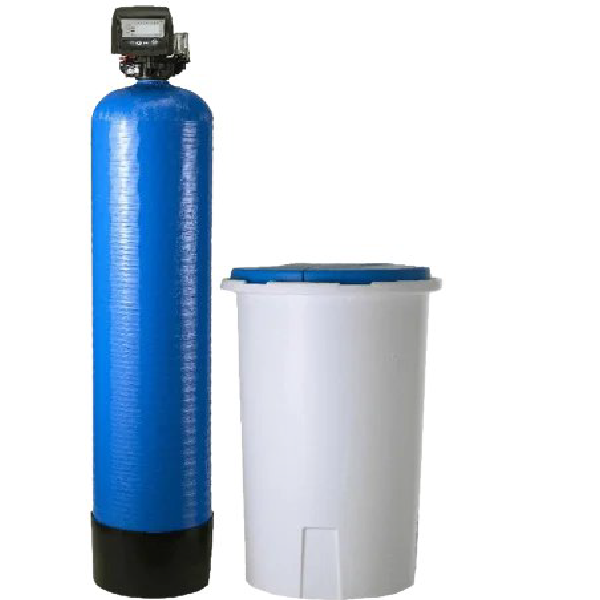

Water Softener
A water softener is primarily used to treat hard water by removing minerals like calcium and magnesium, which can cause problems in both residential and industrial settings. Here’s a breakdown of its application and uses:
Applications of Water Softener :
- Residential Use :
- Commercial Use :
- Agriculture :
- Swimming Pools:
How a Water Softener Works :
Water softeners typically use a resin bed and a process known as ion exchange. Here’s how it works:
Use of a Water Softener :
Benefits of Using a Water Softener :
Would you like to know more about how to select a water softener or how to install one?